UX means the consumer experience design. It considers the interconnection with the company’s goods and services. If there will be a place to link with the experience, be it effective or non-effective, positive or negative, or even neutral, it will change how users communicate. Thus, UX design is the result of the straining of the UI.
UX design has incredible roles, sub-roles, and data to engross. They have to do enormous analysis to know what the users are seeking. Even it requires to be aware of the user’s needs before the users know what they want. Various studies and observations, and conclusions are considered for the pattern usage. Even this is not enough; they must keep swirling between the trends and convenience to select a design to integrate.
The designers will consider a honeycomb in which the center is the users, and all other shells are of the circumstances with the users. It is all about the user’s wants and deeds. The UX designers refer to the experts’ advice who are referring to the laws of UX design formulated by them. They included some laws like users are persuaded by the aesthetics, law of simplicity, law of proximity, etc.
Yet, many UX designs have lots of misconceptions about the designs. It seems easy to get a great UX. But that is not the case. The shuffling between the tabs and then statements in them is a bit reluctant. Learners in their initial time come across numerous myths about the UX designs. But myths are myths. These false beliefs restrict the designers from working efficiently.
Why myths are problematic?
The vast digital world has enormous information out there. That includes myths as well. When there comes a significant number of users, there comes colossal confusion resulting in failed design.
Nowadays, businesses are looking forward to a great extent to develop applications and websites. The Internet is providing a vast platform to thrive in the market. Even the smallest businesses like grocery stores or mega-malls are in search of digital solutions. Similarly, there are vast subjects that are seeking a brilliant UX. These include different kinds of users.
So for them, designers have to start from the very basics. While researching and analyzing, the designers frequently come across various external ideas, which they have accepted without questioning the fact. Moreover, sometimes the theory read may be misunderstood. They might not go in-depth into the statement in order to know the actual meaning of fear, insecurities, or involuntary thoughts. Even one can get confused about the myths and facts.
Here in the blog, we are going to look upon some of the most common myths of UX. It will further help a researcher to understand how to identify a myth and fact. So let us move far to this and clear out the things.
Common myths on UX
UX analyzers must be looking for a lot of designs before they start doing it. User experience circumscribes all the aspects of the users while they make any changes to the solution. Meanwhile, they come across a lot of information while researching. Every day, numerous digital products or services are designed, be it websites, applications, or anything technical. Let us clear out some of the most heard myths.
UX and UI are the same
Those who are not related to this field have always believed that UX and UI are the same things. They think it to be meant for the same purpose, drawing out the same results. But that is wholly a false thought. UI and UX are two different boats of the same river. Both are intended to work for two different results. Let us get it one by one.
UI stands for user interface, which involves designs color, buttons, tabs, content, and user trials. They are subjected to design the tech solutions keeping in mind the user’s encounter. They have to work on computer-integration, augmented reality, smartphones, and UI designs (works for the invisible interfaces) like brightness, sound, and gestures for the solutions.
On the other hand, UX is the next step of the UI. More specifically, it aspires to enhance the end user’s visits while using the technical system. For example, if you are running an eCommerce business, use high quality pictures, it will entice users. You can also make regular photos look amazing by following some techniques.
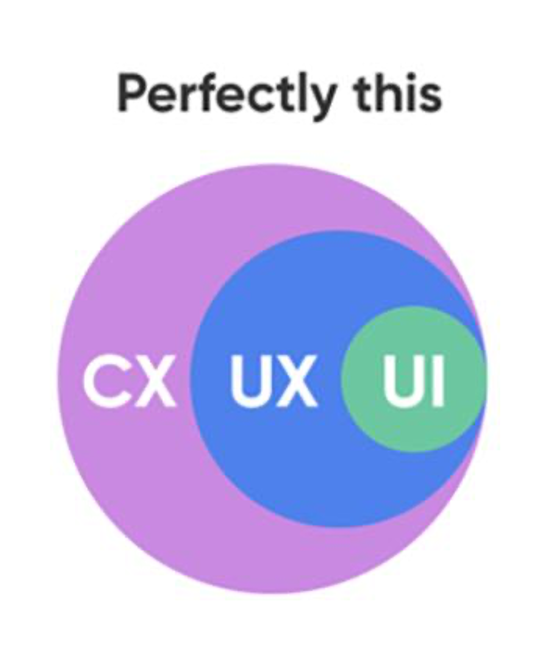
UX sounds more technical; instead, UI is all about the art. Now, let us know how these both are related. Consumer experience (CX) is a whole subject on which a company depends for developing their brand (consider here digital). UX and UI fall under CX. UX is what comes under the subject. And UI is what comes under both of them, though they work for separate results. A designer should know this before opting for both of them.
(uxplanet)
All users are same
The purpose of UX designers is to know the user’s circumstances and improve the brand according to that. So the primary purpose of UX analyzers is to consider the consumers. However, some might fall for the myth that all the users who are using a particular brand expect the same thing. So they think that they will have a standard behavior of the users. But this is falsely interpreted, further resulting in a useless design.
While a company or business is designing a brand, they target vast audiences (mainly) that belong to diverse geographical areas. And this carries out the fact that all users are not the same. The logic, functionalities, purposes, and comfort is varied for the users. Therefore, a designer has to design an app or website for selling, buying, knowledge, awareness, communication, or entertainment.
Even if they choose one category mentioned above, they have to gather different threads. For example, business websites like those who developed a business, their virtual presence could have different kinds of information seekers, some could ask for the products, and others will need to know the brand’s value. So, a retail store seeks a UX analyzer while they hire a source to build a grocery delivery app that can merge all these purposes in their design.
UX designs are going to fill all the possibilities while they consider designing for end-users. However, they should know that all users are not the same.
Just looking good is enough
A UX person should now be familiar with the misconception that looking good is not enough. UX design undoubtedly has to be elegant. However, the fact also says that it has to be operative and functional. Making them attractive could be a reason for a user’s stay to the product or service, but that should even fill the purpose of staying there. It has to be fruitful enough to solve the problems.
UX design has to be functional for the user’s retention. Colors and fonts can not make them stay for long or visit back. The context of the solution is equally important. For example, if the designer is looking for e-commerce UX designs, it should provide a user-friendly process to shop and pay. It should include deep-well research, prototyping, factual, and thoroughly tested to fill the purpose.
Users make optimal choices
Researchers often believe the fact that users are seeking the most informative pieces. But that is not the actual case. In reality, they tend to accept the slightly sensible choice. The majority of the users are not likely to spend significant time getting the most factual answers. Instead, they get satisfied with the partially helping options.
They must first have to be clear in allowing options to the consumers and provide a significant outcome and fill every possible gap on investigating what users (diversely) can expect. Moreover, the latest UX designs in trends can be more specifically made clear to use the optimal designs.
Vast choice increases the chances of user’s satisfaction
Another common misconception here is that the best UX design must include a broad range of options. Actually, vast options can make the design confusing. Users can get lost in that type of design and conclude that it is a useless design. The situation comes like, as the users will have to give themselves more time to make the desired decision, they perhaps skip it and go for the following best options.
Time is essential to every being. Thus, optimize the time for the users, eliminating the complexity of the design. Optimum quality of choices has higher chances to survive. Usability testing is what the experts adopt to conclude. The things that make it possible are quantitative and qualitative testing for the design. These data could help a lot in the sequential design cycle. It will allow the UX persons to drive optimum results.
You should know
UX analyzers don’t need to be creative; they have to be problem solvers and calculative to prepare a great design. A great design needs a lot of hustling and refurbishing. Sensibly, all data available on the Internet are not the apt choice to refer to the designs. Consider all the user’s aspects to filter out facts from the myths to seek out the right thing.
Myths have to be cleared out not just for the current designers but also for future learners. They have to get accurate information to learn and grow. There is so much more to the topic that is yet remaining. But, these are the optimized points that a UX analyzer should be aware of.
Author Bio
Brijesh Vadukiya
Tech activist, blogger, and internet marketing officer of Elluminati Inc for more than three years. My major concern is to educate people who are interested in technology. I am fond of writing useful and informative content that helps brands to grow business.